Terpenes
by Nida Hammad
Last updated: December 3, 2025
Verified and Approved by:
Angela Morris,
MSW, LCSW
Fact Checked

- Terpenes are aromatic compounds that give cannabis its distinctive smell, flavor, and contribute to therapeutic effects alongside cannabinoids
- Over 200 terpenes identified in cannabis, with more than 120 playing significant roles in medical applications
- The entourage effect describes how terpenes work synergistically with THC and CBD to enhance medicinal benefits
- Major terpenes include myrcene (sedating), limonene (uplifting), pinene (focus), linalool (calming), and caryophyllene (pain relief)
- Terpenes are the second most abundant compounds in cannabis after cannabinoids
- Medical benefits range from pain relief and anti-inflammation to anxiety reduction and neuroprotection
- Terpene profiles help patients select strains that match their specific medical needs and desired therapeutic outcomes
- Storage matters: Terpenes degrade with heat, light, humidity, and oxygen exposure
- Full-spectrum products containing diverse terpenes often provide better therapeutic results than isolated cannabinoids
Terpenes: Complete Medical Cannabis Definition & Guide
Terpenes are naturally occurring aromatic compounds found in cannabis and many other plants that produce the distinctive scents, flavors, and therapeutic effects associated with different strains. Terpenes are organic hydrocarbons with the molecular formula (C5H8)n that serve as the primary constituents of essential oils, contributing to both the sensory experience and medicinal properties of medical marijuana. Cannabis contains over 200 identified terpenes, including 58 monoterpenes and 38 sesquiterpenes, making it one of the most terpene-rich plants in nature.
For medical marijuana patients, understanding terpenes is essential because these compounds work synergistically with cannabinoids like THC and CBD to enhance therapeutic effects through what scientists call the “entourage effect.” When you receive your medical marijuana card, budtenders and healthcare providers will help you select products with specific terpene profiles tailored to your medical condition, ensuring you get optimal symptom relief. Terpenes are not just about aroma, they’re active medicinal compounds that can influence everything from pain management to sleep quality to mood regulation.
Unlike cannabinoids, terpenes are found throughout nature in herbs like rosemary and basil, fruits like lemons and mangoes, and trees like pine and eucalyptus. However, cannabis produces uniquely high concentrations of certain therapeutic terpenes in specialized glandular structures called trichomes that appear on female cannabis flowers. The terpene content is what makes each strain distinct, explaining why two cannabis products with identical THC percentages can produce completely different medical effects and patient experiences.
What Are Terpenes?

Terpenes Definition
Terpenes are the largest class of natural products, comprising more than 30,000 identified compounds across all plant species. In cannabis specifically, terpenes are biosynthesized in the same glandular trichomes that produce cannabinoids, creating a complex chemical profile that determines both the strain’s characteristics and its medicinal properties. Chemically, terpenes are hydrocarbons built from five-carbon isoprene units (C5H8) that link together in various configurations to form chains and rings.
The biosynthesis of cannabis terpenes occurs through two distinct metabolic pathways: the methylerythritol phosphate (MEP) pathway in plastids and the mevalonate (MEV) pathway in the cytosol. The MEP pathway converts pyruvate and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate into the building blocks isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP). These precursors are then condensed into longer-chain compounds like geranyl diphosphate (GPP) for monoterpenes and farnesyl diphosphate (FPP) for sesquiterpenes through the action of terpene synthase enzymes.
Cannabis trichomes exist in three distinct morphological types: bulbous (smallest), sessile (short stalk), and stalked (largest and most abundant on mature flowers). Stalked glandular trichomes contain a globular head with more than eight secretory cells and are particularly rich in cannabinoids and monoterpenes. Sessile trichomes, found mainly on sugar leaves, produce higher proportions of sesquiterpenes. This specialized production system allows cannabis to generate extraordinarily diverse terpene profiles that vary by genetics, environmental conditions, and growth stage.
Key Characteristics of Terpenes:
- Aromatic compounds responsible for the distinctive smells ranging from citrus and pine to earthy and diesel
- Volatile organic compounds that easily evaporate at room temperature, creating the cannabis aroma
- Lipophilic molecules that are highly non-polar, insoluble in water, and readily absorbed through biological membranes
- Thermally sensitive with boiling points ranging from 110°C to 220°C depending on molecular size
- Produced as secondary metabolites that protect plants from predators, attract pollinators, and defend against environmental stress
- Classified by carbon count: monoterpenes (C10), sesquiterpenes (C15), diterpenes (C20), triterpenes (C30)
The term “terpene” is often used interchangeably with “terpenoid,” though technically terpenoids are modified terpenes containing additional functional groups (usually oxygen) through oxidation during drying and curing. Most cannabis products contain both terpenes and terpenoids, with the distinction being relatively minor for medical marijuana patients. What matters most is understanding how these aromatic compounds contribute to therapeutic effects.
How Terpenes Relate to Medical Marijuana

Medical marijuana patients interact with terpenes every time they use cannabis, whether smoking flower, vaping concentrates, or consuming terpene-rich full-spectrum oils. Understanding terpene profiles helps patients choose products that provide targeted symptom relief without unwanted side effects. Terpenes modulate how cannabinoids interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system, potentially increasing therapeutic benefits while reducing adverse reactions like anxiety or sedation.
Medical Applications:
Terpenes are particularly important for medical cannabis because:
- Enhanced Therapeutic Effects Through the Entourage Effect: Terpenes work synergistically with cannabinoids to produce effects greater than the sum of individual compounds. Research suggests that full-spectrum cannabis products containing diverse terpenes provide more balanced, effective symptom relief compared to isolated THC or CBD. For example, the terpene myrcene may enhance THC’s ability to cross the blood-brain barrier, increasing its analgesic and sedative properties. Beta-caryophyllene directly activates CB2 cannabinoid receptors, providing anti-inflammatory effects independent of THC or CBD. Limonene appears to boost serotonin and dopamine levels, complementing CBD’s anxiolytic properties. This synergistic interaction allows medical cannabis physicians to recommend lower cannabinoid doses while achieving better therapeutic outcomes, reducing the risk of side effects like cognitive impairment or tolerance development.
- Targeted Treatment Based on Terpene Profiles: Different terpene combinations produce distinct therapeutic effects, allowing personalized medicine approaches. Patients with chronic pain often benefit from strains high in myrcene, caryophyllene, and linalool, which provide analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and muscle-relaxant properties. Those with anxiety disorders may prefer limonene-dominant strains that offer mood elevation without sedation, or linalool-rich varieties that promote calming effects similar to lavender aromatherapy. Patients seeking daytime symptom relief typically choose pinene and limonene-heavy strains that enhance alertness and mental clarity while reducing inflammation. Terpene profiles also help predict tolerance development, strains with diverse terpene content may be less likely to cause rapid tolerance compared to THC isolates, as multiple pathways contribute to therapeutic effects.
- Modulation of Side Effects and Psychoactivity: Terpenes can mitigate unwanted cannabinoid effects while preserving medical benefits. Pinene acts as an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, potentially counteracting THC-induced short-term memory impairment. Limonene may reduce THC-related anxiety through its anxiolytic properties and mood-elevating effects. CBD-rich strains with high linalool content offer anti-anxiety benefits with minimal psychoactivity, ideal for patients who cannot tolerate THC’s intoxicating effects. Conversely, myrcene at concentrations above 0.5% can enhance sedation and produce “couch-lock” effects, beneficial for insomnia but problematic for daytime use. Understanding these interactions allows patients and physicians to fine-tune treatment regimens, maximizing therapeutic benefits while minimizing adverse reactions.
Clinical Perspective:
Medical cannabis physicians consider terpene profiles when recommending products for specific conditions. Patients with chronic pain conditions like fibromyalgia, neuropathy, or cancer-related pain often benefit from strains containing myrcene (analgesic), caryophyllene (anti-inflammatory, pain signal inhibition), and linalool (muscle relaxation). Those with anxiety disorders, PTSD, or depression typically respond well to limonene (mood elevation, stress reduction) and linalool (calming, anxiolytic effects) dominant profiles. Patients requiring anti-inflammatory treatment for conditions like arthritis, Crohn’s disease, or multiple sclerosis may see optimal results with caryophyllene and humulene, both of which interact with inflammation pathways.
For sleep disorders and insomnia, high-myrcene strains with sedating terpinolene provide strong sedative effects and prolonged sleep duration. Patients with neurodegenerative conditions like Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s disease may benefit from pinene’s potential neuroprotective properties and memory-enhancement effects. Those undergoing chemotherapy often prefer limonene-rich products for anti-nausea benefits combined with mood elevation to combat treatment-related depression.
It’s important to note that most current terpene research is preclinical, based on laboratory studies rather than large-scale human clinical trials. The concentrations used in these studies often exceed what patients typically consume through regular cannabis use. While the therapeutic potential is promising, medical cannabis providers should present terpene benefits with appropriate scientific caution, acknowledging the early stage of research while still recognizing their clinical value in personalized treatment approaches.
Terpenes Medical Marijuana Card

Once you receive your medical marijuana card, you’ll have legal access to products with detailed lab-tested terpene profiles from licensed dispensaries. Medical dispensaries provide comprehensive cannabinoid and terpene analysis on product labels, typically listing the three most prevalent terpenes and their concentrations (usually around 1-3% total terpene content). This information empowers you to make informed decisions about which products best match your medical needs and desired therapeutic outcomes.
What You Can Access:
With your medical card, you can:
- Purchase medical-grade cannabis with verified terpene profiles from state-licensed dispensaries that conduct third-party laboratory testing, ensuring product safety, potency, and accurate terpene content information
- Receive expert guidance from medical budtenders trained in cannabis therapeutics who can recommend specific terpene profiles for your qualifying condition, symptom severity, and treatment goals
- Access a wider variety of terpene-rich products including live resin concentrates, full-spectrum oils, and carefully cultivated flower with preserved terpene content that recreational products may lack
- Benefit from personalized treatment plans where physicians and dispensary staff consider your terpene preferences alongside cannabinoid ratios to optimize symptom management
- Pay lower taxes compared to recreational purchasers in most medical marijuana states, making high-quality terpene-rich products more affordable
- Obtain higher potency products with elevated terpene concentrations that may exceed recreational limits, providing enhanced therapeutic benefits
Getting your medical marijuana card is fast and easy with Leafy DOC. Our licensed physicians can evaluate your qualifying condition and provide your terpene-optimized cannabis recommendation in minutes, all online. We understand that different conditions respond to different terpene profiles, and our medical team will help you identify the best starting point for your personalized treatment journey.
Major Cannabis Terpenes Effects & Medical Benefits
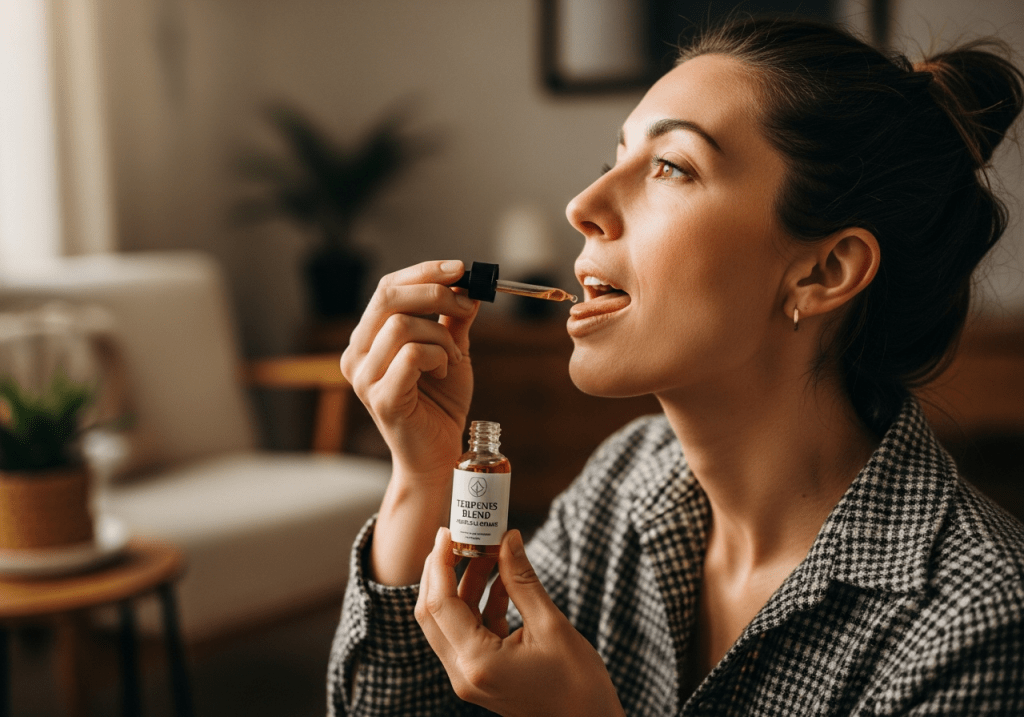

| Terpene | Aroma | Effects | Boiling Point | Common Cannabis Strains |
|---|
| Pinene | Pine, woodsy | Anti-inflammatory, anti-bacterial, bronchial dilator | 311°F | Haze Berry, OG Kush, Blue Dream |
| Humulene | Spicy, herbal | Anti-inflammatory, appetite suppressant | 222.8°F | Gelato, Atlantis, Sour Diesel |
| Limonene | Citrus | Uplifting, anti-anxiety, anti-depressant | 348.8°F | Wedding Cake, Quantum Kush, Berry White |
| Myrcene | Earthy, musk, fruity | Relaxation, euphoria, “couch-lock” | 332.6°F | OG Kush, Girl Scout Cookies, Grape Ape |
| Borneol | Mint, metallic | Anti-inflammatory, analgesic | 415.4°F | K-13 Haze, Golden Haze, Amnesia Haze |
| Phytol | Floral | Sedative, anti-anxiety, anti-inflammatory | 399.2°F | Sour Diesel, Blue Dream, Cheese |
| Eucalyptol | Minty, menthol | Anti-bacterial, anti-fungal | 341.6°F | Girl Scout Cookies, AC/DC, Headband |
| Sabinene | Woodsy, spicy, peppery | Digestive aid, anti-bacterial, antioxidant | 326.4°F | Super Silver Haze |
Cannabis contains over 200 identified terpenes, but a handful of major terpenes appear in significant concentrations and provide the most well-studied therapeutic effects. Understanding these primary terpenes helps medical marijuana patients select products that target their specific symptoms and medical conditions.
Myrcene (β-Myrcene)
Aroma: Earthy, musky, clove-like with herbal notes similar to hops and thyme
Boiling Point: 332.6°F (167°C)
Concentration Threshold: Effects become pronounced above 0.5% by weight
Myrcene is the most abundant terpene in most cannabis strains, often accounting for over 50% of total terpene content. This monoterpene is found naturally in hops (used in beer production), mangoes, lemongrass, and bay leaves. Myrcene’s sedating properties make it particularly valuable for medical conditions requiring relaxation, pain relief, and sleep support.
Medical Effects:
- Powerful Analgesic Properties: Myrcene activates opioid pathways in the brain through α2-adrenergic receptor mechanisms, providing pain relief comparable to some pharmaceutical analgesics without addiction potential
- Muscle Relaxant: Reduces muscle tension and spasms, beneficial for fibromyalgia, multiple sclerosis, and sports injuries
- Enhanced Cannabinoid Absorption: Increases permeability of cell membranes, allowing cannabinoids to cross the blood-brain barrier more efficiently and intensifying overall therapeutic effects
- Sedation and “Couch-Lock”: Produces full-body relaxation and drowsiness at concentrations above 0.5%, making it excellent for insomnia but potentially problematic for daytime use
- Anti-inflammatory: Reduces inflammatory markers and may protect tissues from oxidative damage, though effects are based on higher concentrations than typical consumption
Medical Conditions: Chronic pain, insomnia, muscle spasms, inflammation, anxiety
Common Strains High in Myrcene: OG Kush, Girl Scout Cookies, Grape Ape, Blue Dream, Granddaddy Purple
Limonene (D-Limonene)
Aroma: Bright citrus, lemon, orange peel
Boiling Point: 348.8°F (176°C)
Limonene is the second most common terpene in nature and one of the most prevalent in cannabis. This monoterpene gives citrus fruits their characteristic smell and is widely used in cleaning products, cosmetics, and food flavoring. In medical cannabis, limonene provides mood-elevating and anti-anxiety benefits that complement cannabinoid therapy.
Medical Effects:
- Mood Enhancement and Anti-Depression: Boosts serotonin and dopamine neurotransmitter levels, providing natural mood elevation and potential antidepressant effects
- Anxiolytic Properties: Reduces anxiety and stress through multiple pathways, making it valuable for generalized anxiety disorder, social anxiety, and panic disorder
- Enhanced Transdermal Absorption: Improves skin penetration of other compounds, beneficial for topical cannabis applications
- Anti-Cancer Potential: Laboratory studies suggest limonene may have anti-tumor properties, though human research is limited
- Gastric Reflux Relief: May help with GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease) and digestive discomfort
- Antioxidant Activity: Protects cells from oxidative stress and potential damage
Medical Conditions: Depression, anxiety disorders, PTSD, stress-related conditions, GERD, inflammation
Common Strains High in Limonene: Wedding Cake, Quantum Kush, Berry White, Durban Poison, Super Lemon Haze
Pinene (α-Pinene and β-Pinene)
Aroma: Pine, turpentine, woody, fresh forest
Boiling Point: 311°F (155°C)
Pinene exists in two isomers, alpha-pinene and beta-pinene, both abundant in coniferous trees, rosemary, basil, and parsley. This monoterpene is the most widespread terpene in nature and the major component of turpentine. In medical cannabis, pinene offers unique cognitive and respiratory benefits.
Medical Effects:
- Memory Enhancement and Neuroprotection: Acts as an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, potentially counteracting THC-induced short-term memory impairment and supporting cognitive function
- Bronchodilator: Opens airways and improves respiratory function, beneficial for asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Anti-inflammatory: Reduces inflammatory markers through multiple pathways
- Antimicrobial and Antiseptic: Exhibits antibacterial and antifungal properties
- Alertness and Focus: Promotes mental clarity and concentration without stimulant side effects
- Potential Anti-Cancer Properties: Early research suggests pinene may have anti-tumor effects, particularly in lung cancer cells
Medical Conditions: Memory impairment, respiratory conditions, inflammation, bacterial infections, cognitive disorders
Common Strains High in Pinene: Haze Berry, OG Kush, Blue Dream, Jack Herer, Dutch Treat
Linalool
Aroma: Floral, lavender, spicy with slight citrus notes
Boiling Point: 388.4°F (198°C)
Linalool is the terpene responsible for lavender’s calming aroma and is widely used in aromatherapy products. Found in lavender, mint, cinnamon, and birch, linalool provides powerful anti-anxiety and sedative effects that make it valuable for stress-related medical conditions.
Medical Effects:
- Anxiolytic and Stress Reduction: Significantly reduces anxiety through GABAergic mechanisms similar to benzodiazepines but without addiction potential or severe side effects
- Sedative Properties: Promotes relaxation and sleep onset, beneficial for insomnia and sleep disorders
- Pain Relief: Provides analgesic effects through opioid system modulation and local anesthetic properties
- Anti-inflammatory: Reduces inflammation markers and immune system overactivity
- Neuroprotective: May protect brain cells from damage and shows potential in Alzheimer’s disease research
- Anti-Convulsant: Reduces seizure activity in some epilepsy models
- Aromatherapy Benefits: Inhalation alone can produce calming effects even without cannabinoid consumption
Medical Conditions: Anxiety disorders, PTSD, insomnia, chronic pain, epilepsy, neurodegenerative diseases
Common Strains High in Linalool: Lavender, LA Confidential, Amnesia Haze, Special Kush
Beta-Caryophyllene (β-Caryophyllene)
Aroma: Spicy, peppery, woody with clove notes
Boiling Point: 266°F (130°C)
Beta-caryophyllene is unique among terpenes because it directly activates cannabinoid receptors, specifically the CB2 receptor, making it the only terpene that functions as a cannabinoid. This sesquiterpene is found in black pepper, cloves, cinnamon, and hops, and provides powerful anti-inflammatory benefits without psychoactive effects.
Medical Effects:
- CB2 Receptor Activation: Directly binds to CB2 cannabinoid receptors throughout the body, producing anti-inflammatory effects without psychoactivity
- Pain Signal Inhibition: Affects transmission of pain signals along peripheral nerves, providing relief for neuropathic pain
- Anti-inflammatory: Reduces inflammation through cannabinoid receptor pathways and other mechanisms
- Gastroprotective: Protects stomach lining and may benefit gastric ulcers and inflammatory bowel disease
- Anti-anxiety and Anti-Depression: Modulates stress response and mood regulation
- Neuroprotective: May protect brain cells from oxidative stress and neurodegenerative processes
- Potential Anti-Cancer: Laboratory studies show promise in reducing tumor growth, though human research is needed
Medical Conditions: Chronic pain, inflammation, arthritis, Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, neuropathy, anxiety, depression
Common Strains High in Caryophyllene: Girl Scout Cookies, Sour Diesel, Chemdog, Original Glue (GG4), Bubba Kush
Humulene (α-Humulene)
Aroma: Earthy, woody, spicy with herbal notes
Boiling Point: 222.8°F (106°C)
Humulene is found in hops (Humulus lupulus, hence the name), ginseng, ginger, and sage. This sesquiterpene provides unique appetite-suppressing properties that distinguish it from other cannabis terpenes, along with significant anti-inflammatory benefits.
Medical Effects:
- Appetite Suppression: Unlike most cannabinoids and terpenes, humulene may reduce appetite, potentially beneficial for weight management
- Anti-inflammatory: Affects inflammation pathways associated with allergic responses and asthma
- Antibacterial: Shows activity against various bacterial strains
- Potential Anti-Cancer: Early research explores tumor-reducing properties, though evidence remains preliminary
- Pain Relief: Provides analgesic effects through anti-inflammatory mechanisms
Medical Conditions: Inflammatory conditions, allergies, asthma, bacterial infections, obesity-related complications
Common Strains High in Humulene: Gelato, Atlantis, Sour Diesel, White Widow, Headband
Terpinolene
Aroma: Fresh, piney, floral with hints of citrus and herbs
Boiling Point: 366°F (186°C)
Terpinolene is less common than other major terpenes but creates a distinctive profile when present in high concentrations. Found in nutmeg, tea tree, conifers, and apples, terpinolene provides a complex aromatic experience and unique therapeutic properties.
Medical Effects:
- Sedative Properties: Promotes relaxation and sleep despite its fresh, uplifting aroma
- Antioxidant: Protects cells from oxidative damage and free radical formation
- Anticancer Potential: Shows promise in laboratory studies for reducing tumor growth, particularly in brain and lung cancer cells
- Antibacterial and Antifungal: Exhibits antimicrobial properties
- Central Nervous System Depressant: Reduces nervous system activity, contributing to calming effects
Medical Conditions: Insomnia, anxiety, oxidative stress conditions, bacterial infections
Common Strains High in Terpinolene: Jack Herer, Dutch Treat, XJ-13, Golden Pineapple
Secondary Terpenes: Supporting Therapeutic Effects

Beyond the major terpenes, cannabis contains numerous secondary terpenes that appear in lower concentrations but still contribute to the entourage effect and overall therapeutic profile. These compounds add complexity to the aroma, flavor, and medicinal properties of different strains.
Borneol
Aroma: Minty, camphor-like with metallic undertones
Effects: Sedative, analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial
Found In: Rosemary, mint, camphor
Strains: K13-Haze, Golden Haze, Amnesia Haze
Eucalyptol (Cineole)
Aroma: Cooling menthol, spicy, minty
Effects: Anti-inflammatory, pain relief, antifungal, antimicrobial
Found In: Eucalyptus, tea tree, sage
Strains: Girl Scout Cookies, AC/DC, Headband
Phytol
Aroma: Sweet floral fragrance
Effects: Sedative, anti-anxiety, anti-inflammatory, promotes healthy sleep
Found In: Jasmine flowers, green tea, white cabbage
Strains: Sour Diesel, Blue Dream, Cheese
Bisabolol (α-Bisabolol)
Aroma: Floral, sweet, delicate
Effects: Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antimicrobial, skin healing
Found In: Chamomile, candeia tree
Medical Applications: Skin conditions, inflammation, wound healing
Camphene
Aroma: Earthy, musky with fir needle notes
Effects: Antifungal, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory
Found In: Fir needles, camphor oil, rosemary
Medical Applications: Fungal infections, bacterial infections, cardiovascular health
Sabinene
Aroma: Spicy, woody, peppery with citrus notes (some describe it as pumpkin pie-like)
Effects: Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, digestive aid
Found In: Norway spruce, black pepper, nutmeg
Strains: Super Silver Haze
Valencene
Aroma: Sweet citrus, orange
Effects: Anti-inflammatory, insect repellent, potential anti-skin cancer properties
Found In: Valencia oranges, grapefruits, tangerines
Medical Applications: Inflammation, skin protection
Delta-3-Carene
Aroma: Sweet, pungent, citrus with pine notes
Effects: Anti-inflammatory, bone health support, drying of bodily fluids
Found In: Pine, cedar, rosemary
Medical Applications: Bone fractures, osteoporosis, excessive mucus production
Guaiol
Aroma: Pine, woody, rose-like
Effects: Anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial
Found In: Guaiacum plant, cypress pine
Medical Applications: Inflammation, infections
Phellandrene
Aroma: Citrus, peppery, minty
Effects: Antifungal, antibacterial, potential anticancer properties
Found In: Eucalyptus, dill, parsley, gingergrass
Medical Applications: Fungal infections, digestive health
The Entourage Effect: How Terpenes Work With Cannabinoids

The entourage effect is the hypothesis that cannabis compounds work synergistically, producing therapeutic effects greater than any single compound alone. Introduced by researchers Raphael Mechoulam and Shimon Ben-Shabat in 1998, this concept suggests that cannabinoids (THC, CBD, CBG, etc.), terpenes, flavonoids, and other phytochemicals interact to modulate cannabis effects on the human body.
How the Entourage Effect Works:
Terpenes may influence the entourage effect through several mechanisms:
- Modulation of Cannabinoid Receptor Activity: Some terpenes like beta-caryophyllene directly activate cannabinoid receptors. Others may affect how THC and CBD bind to CB1 and CB2 receptors, altering their efficacy and downstream effects.
- Neurotransmitter System Interactions: Terpenes interact with various neurotransmitter systems beyond the endocannabinoid system. Limonene affects serotonin and dopamine pathways, linalool modulates GABA receptors, and pinene inhibits acetylcholinesterase. These interactions complement cannabinoid effects and create complex therapeutic profiles.
- Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability: Myrcene increases permeability of biological membranes, potentially enhancing how much THC and other cannabinoids reach the brain and other tissues. This could explain why high-myrcene strains produce stronger psychoactive and sedative effects even with similar THC content.
- Anti-inflammatory Synergy: Multiple terpenes (caryophyllene, humulene, linalool, pinene) provide anti-inflammatory effects through different pathways. When combined with anti-inflammatory cannabinoids like CBD and CBG, the overall anti-inflammatory response may be more comprehensive and effective.
- Side Effect Mitigation: Terpenes may reduce unwanted cannabinoid effects. Pinene’s acetylcholinesterase inhibition potentially counteracts THC-induced memory impairment. Limonene’s anxiolytic properties may reduce THC-related anxiety in susceptible individuals.
Scientific Evidence and Limitations:
While the entourage effect concept is popular among cannabis consumers and many medical practitioners, the scientific evidence remains limited and somewhat controversial. Most supporting research comes from preclinical laboratory studies rather than rigorous human clinical trials. Some researchers caution that claims about the entourage effect may be overstated, noting that:
- Terpene concentrations in cannabis are much lower than cannabinoid concentrations, raising questions about whether they reach pharmacologically relevant doses
- Human studies are scarce, with most evidence extrapolated from in vitro (test tube) or animal research
- Placebo effects and expectations may contribute to perceived differences between full-spectrum and isolate products
- Individual variation in metabolism, receptor sensitivity, and baseline biochemistry complicates universal claims about terpene effects
Despite these limitations, many medical marijuana patients and clinicians report that full-spectrum products containing diverse terpenes provide more balanced, effective symptom relief compared to isolated THC or CBD. This clinical observation, combined with growing preclinical evidence, supports the therapeutic value of terpene-rich cannabis products even as researchers continue investigating the exact mechanisms.
Learn How to Make Cannabis Infused Olive Oil for Cooking
How to Use Terpenes Safely for Medical Cannabis Treatment

Understanding terpene safety, proper dosing, and consumption methods helps medical marijuana patients maximize therapeutic benefits while minimizing potential side effects.
Selecting Products Based on Terpene Profiles:
- Read Laboratory Test Results: Look for products with comprehensive lab testing that lists cannabinoid and terpene content. Terpene percentages typically range from 1-3% total, with individual terpenes comprising 0.1-1% each.
- Match Terpenes to Medical Goals:
- Pain Relief: High myrcene, caryophyllene, linalool
- Anxiety/Stress: High limonene, linalool, low-THC profiles
- Sleep/Insomnia: High myrcene, linalool, terpinolene
- Focus/Alertness: High pinene, limonene, low myrcene
- Inflammation: High caryophyllene, humulene, pinene
- Mood Enhancement: High limonene, pinene
- Check Product Freshness: Terpenes are volatile and degrade over time. Choose products with recent package dates and strong, fresh aromas indicating high terpene content.
Consumption Methods That Preserve Terpenes:
- Vaporization at Low Temperatures (315-400°F): Best preserves terpenes while activating cannabinoids. Different terpenes have different boiling points, so temperature control matters.
- Smoking Flower: Provides full terpene profile but high heat may degrade some delicate terpenes and create potentially harmful combustion byproducts.
- Full-Spectrum Oils and Tinctures: Contain preserved terpenes when extracted properly using methods like CO2 extraction at low temperatures.
- Live Resin Concentrates: Made from flash-frozen fresh cannabis, preserving maximum terpene content (often 5-10% total terpenes).
- Edibles: Generally lack significant terpenes unless specifically added. Terpenes are destroyed during most cooking processes.
Safety Considerations:
- Avoid High-Heat Dabbing: Temperatures above 450°F may degrade terpenes into potentially harmful compounds. Stick to low-temperature dabbing if using concentrates.
- Be Cautious With Synthetic Terpenes: Some vape cartridges use synthetic terpenes or botanical terpenes from non-cannabis sources. Natural cannabis-derived terpenes are preferable, though research on safety differences is limited.
- Start Low With High-Terpene Products: Terpene-rich products may produce stronger effects than expected. Begin with small doses and gradually increase.
- Monitor for Allergic Reactions: Some individuals may be sensitive to specific terpenes, experiencing skin irritation, respiratory symptoms, or headaches. Discontinue use if adverse reactions occur.
- Consider Drug Interactions: Terpenes may interact with medications. Consult your physician before combining terpene-rich cannabis with prescription drugs, especially sedatives, antidepressants, or anti-inflammatory medications.
Proper Storage to Maintain Terpene Content:
- Cool Temperatures: Store cannabis in cool environments (60-70°F) away from heat sources
- Minimal Light Exposure: Use opaque containers and store in dark locations
- Low Humidity: Maintain 55-62% relative humidity using humidity control packs
- Limited Oxygen: Use airtight containers to prevent oxidation and terpene degradation
- Avoid Plastic: Glass jars preserve terpenes better than plastic containers
Dosing Guidelines:
Unlike cannabinoids, terpenes don’t have established medical dosing guidelines. Research suggests meaningful biological effects may require concentrations above 0.05% by weight in full-spectrum extracts. For reference:
- Typical flower: 1-3% total terpenes
- High-terpene flower: 3-5% total terpenes
- Live resin concentrates: 5-10% total terpenes
- Isolated terpenes (not recommended for beginners): Can be added to products but require extreme caution due to high potency
Most medical marijuana patients benefit from simply selecting strains with appropriate terpene profiles rather than calculating precise terpene doses. Your budtender can guide you toward products with terpene concentrations suitable for your experience level and medical needs.
Terpene Profiles by Medical Condition

Different medical conditions respond optimally to specific terpene combinations. This guide helps patients and physicians select appropriate terpene profiles for various qualifying conditions.
Chronic Pain:
- Primary Terpenes: Myrcene (analgesic), caryophyllene (pain signal inhibition), linalool (muscle relaxation)
- Secondary Terpenes: Humulene (anti-inflammatory), pinene (anti-inflammatory)
- Recommended Strains: OG Kush, Bubba Kush, Northern Lights, Grape Ape
Limonene (mood elevation), linalool (anxiolytic), low myrcene (avoid excessive sedation)
- Secondary Terpenes: Pinene (mental clarity), caryophyllene (stress reduction)
- Recommended Strains: Harlequin, Cannatonic, Jack Herer, Super Lemon Haze
Insomnia and Sleep Disorders:
- Primary Terpenes: High myrcene (sedation), linalool (sleep onset), terpinolene (CNS depression)
- Secondary Terpenes: Phytol (sleep promotion), borneol (sedative)
- Recommended Strains: Granddaddy Purple, Northern Lights, Purple Kush, Blackberry Kush
Depression:
- Primary Terpenes: Limonene (mood enhancement), pinene (alertness), low sedating terpenes
- Secondary Terpenes: Beta-caryophyllene (mood regulation)
- Recommended Strains: Super Lemon Haze, Durban Poison, Tangie, Strawberry Cough
PTSD:
- Primary Terpenes: Linalool (anxiety relief), limonene (mood stabilization), myrcene (stress reduction)
- Secondary Terpenes: Pinene (memory function support)
- Recommended Strains: Purple Urkle, Blue Dream, OG Kush, Pineapple Express
Inflammatory Conditions (Arthritis, Crohn’s, IBD):
- Primary Terpenes: Caryophyllene (CB2 activation), humulene (inflammation pathways), myrcene (anti-inflammatory)
- Secondary Terpenes: Pinene, linalool, eucalyptol
- Recommended Strains: ACDC, Girl Scout Cookies, Sour Diesel, Harlequin
Nausea and Appetite Loss:
- Primary Terpenes: Limonene (anti-nausea), low humulene (avoid appetite suppression)
- Secondary Terpenes: Myrcene (may enhance cannabinoid effects)
- Recommended Strains: Lemon Haze, Tangie, Durban Poison
Neurodegenerative Conditions (Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s):
- Primary Terpenes: Pinene (neuroprotection, memory), linalool (neuroprotection), caryophyllene (anti-oxidative stress)
- Secondary Terpenes: Limonene (cognitive support)
- Recommended Strains: Haze strains, Jack Herer, Sour Diesel
Seizure Disorders:
- Primary Terpenes: Linalool (anticonvulsant), low THC/high CBD ratios
- Secondary Terpenes: Myrcene, caryophyllene
- Recommended Strains: Charlotte’s Web, ACDC, Ringo’s Gift
Related Cannabis Terms
Understanding terpenes is easier when you also know these related terms:
Directly Related Terms:
- Terpenoids – Modified terpenes containing additional functional groups through oxidation; often used interchangeably with terpenes
- Cannabinoids – Chemical compounds like THC and CBD that interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system and work synergistically with terpenes
- Trichomes – Glandular structures on cannabis flowers where terpenes and cannabinoids are produced and stored
- Entourage Effect – The synergistic interaction between terpenes, cannabinoids, and other cannabis compounds that enhances therapeutic effects
- Full-Spectrum – Cannabis products containing the complete profile of cannabinoids, terpenes, and other phytochemicals rather than isolated compounds
Compare & Contrast:
- Terpenes vs Flavonoids – Both are aromatic plant compounds, but flavonoids provide color and different therapeutic properties
- Live Resin vs Cured Cannabis – Live resin preserves maximum terpenes through flash-freezing; cured cannabis has reduced terpene content
- Isolate vs Full-Spectrum – Isolates contain single cannabinoids without terpenes; full-spectrum includes complete plant profile
Learn More About:
- Essential Oils – Natural extracts rich in terpenes used for aromatherapy and medicinal purposes
- Strain Types – Indica, Sativa, and Hybrid classifications partially determined by terpene profiles
- Cannabis Extraction Methods – CO2, ethanol, and hydrocarbon methods that affect terpene preservation
- Vaporization – Consumption method that preserves terpenes better than smoking
- Lab Testing – Third-party analysis that quantifies cannabinoid and terpene content
Complete Cannabis 101 Glossary
Qualifying Conditions for Medical Cannabis
Terpene-rich medical cannabis can help treat many qualifying conditions. If you have any of the following conditions, you may be eligible for a medical marijuana card:
- Chronic Pain
- Anxiety Disorders
- PTSD
- Chronic Kidney Disease
- Epilepsy
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Crohn’s Disease
- Diabetes
- Insomnia
- Depression
- Neuropathy
- Parkinson’s
- Alzheimer’s Disease
- Glaucoma
- HIV/AIDS
See Full List of Qualifying Conditions →
Not sure if you qualify? Talk to our doctor to check the eligibility.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between terpenes and cannabinoids?
Terpenes are aromatic compounds giving cannabis its smell and flavor, with therapeutic effects. Cannabinoids (like THC and CBD) interact directly with the endocannabinoid system and are responsible for psychoactive effects. Terpenes can enhance or modulate how cannabinoids affect the body.
Do terpenes get you high?
No, terpenes are generally non-psychoactive. They can influence mood, relaxation, or alertness and modify THC’s effects, making highs more sedating or uplifting depending on the terpene.
Which terpenes are best for pain relief?
Myrcene: Pain relief through opioid pathways; good for chronic pain.
Beta-caryophyllene: Activates CB2 receptors, reduces inflammatory pain.
Linalool: Analgesic and muscle relaxant; helps with tension-related pain.
Can terpenes help with anxiety without THC?
Yes.
Linalool: Calms via GABA modulation.
Limonene: Uplifts mood, reduces stress.
Beta-caryophyllene: Modulates stress through CB2 receptors.
CBD products with these terpenes are effective without THC.
How long do terpenes last in cannabis?
Well-stored flower: 6–12 months.
Concentrates: 1–2 years.
Factors affecting degradation: Heat, light, oxygen, humidity.
Store in airtight glass jars in a cool, dark place.
Are synthetic terpenes safe?
Synthetic terpenes are chemically identical to natural ones but may produce harmful byproducts when heated. Prefer natural, cannabis-derived terpenes and choose reputable brands with testing.
7. Which terpenes should I avoid if I need to stay alert?
Avoid sedating terpenes like myrcene, linalool, and terpinolene.
Better choices for focus: pinene, limonene, or low-myrcene sativa strains.

Get Approved for Your Medical Marijuana Card in Minutes!

-
THC Design. (n.d.). It’s all about the terpenes. THC Design. https://thcdesign.com/blog/its-all-about-the-terpenes/ THC Design
-
The Healing Clinics. (n.d.). The (semi‑)complete list of cannabis terpenes. The Healing Clinics. https://www.thehealingclinics.com/the-semi-complete-list-of-cannabis-terpenes/
-
URHemped. (n.d.). List of terpenes and effects – Know all about it. URHemped. https://urhemped.com/blogs/cbd-benefits/list-of-terpenes-and-effects-know-all-about-it?srsltid=AfmBOoodSLGGNnYMo5a3KJRzyYrAm07c1PVSJCOd10DOwfdQzc-Gpqv2
-
Leafwell. (n.d.). Terpenes. Leafwell. https://leafwell.com/blog/terpenes
-
SafeLeaf. (n.d.). Terpenes — are they safe? SafeLeaf. https://www.safeleaf.ca/terpenes-are-they-safe/
-
CompCareMD. (n.d.). List of cannabis terpenes and their effects. CompCareMD. https://compcaremd.com/list-of-cannabis-terpenes-and-their-effects/
-
MellowFellow. (n.d.). The complete list of cannabis terpenes and their effects. MellowFellow. https://mellowfellow.fun/blogs/learn/the-complete-list-of-cannabis-terpenes-and-their-effects
-
GoodRx. (n.d.). Terpene guide. GoodRx. https://www.goodrx.com/health-topic/cannabis/terpene-guide?srsltid=AfmBOooMDsMqYNmvUH9bWEPuZX-u-rc9JK24n95iV0QdXfvOd6xT5gNs
-
Healthline. (n.d.). Cannabis terpenes. Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/cannabis-terpenes
-
Curaleaf Clinic. (n.d.). Understanding the role of terpenes in medical cannabis. Curaleaf Clinic. https://curaleafclinic.com/understanding-the-role-of-terpenes-in-medical-cannabis/
Our Commitment to Medical Accuracy
At Leafy DOC, every piece of content is created with care and reviewed by licensed medical professionals. Our experts ensure that health information is not only evidence-based but also easy to understand and practical for everyday life. We regularly update our resources to reflect the latest research, so you can make informed decisions about your wellness journey with confidence.
Reviewed by
Dr. Hannah Russo, MD, MPH
Dr. Hannah Russo is an internal medicine doctor and public health advocate with extensive experience in telemedicine and cannabis education. Her work bridges clinical practice and digital health, ensuring that patients receive safe, informed, and convenient care. She is passionate about expanding access to natural, evidence-based therapies for chronic conditions.

Written by :
Nida Hammad
Last Updated :
December 3, 2025