What Does A Marijuana Plant Look Like ?
by Nida Hammad · November 3, 2023
Curious about what a marijuana plant actually looks like? Feast your eyes on the stunning visuals of vibrant green leaves and potent buds. Don’t miss out on this visual guide – click here to discover the hidden beauty of marijuana plants!

-
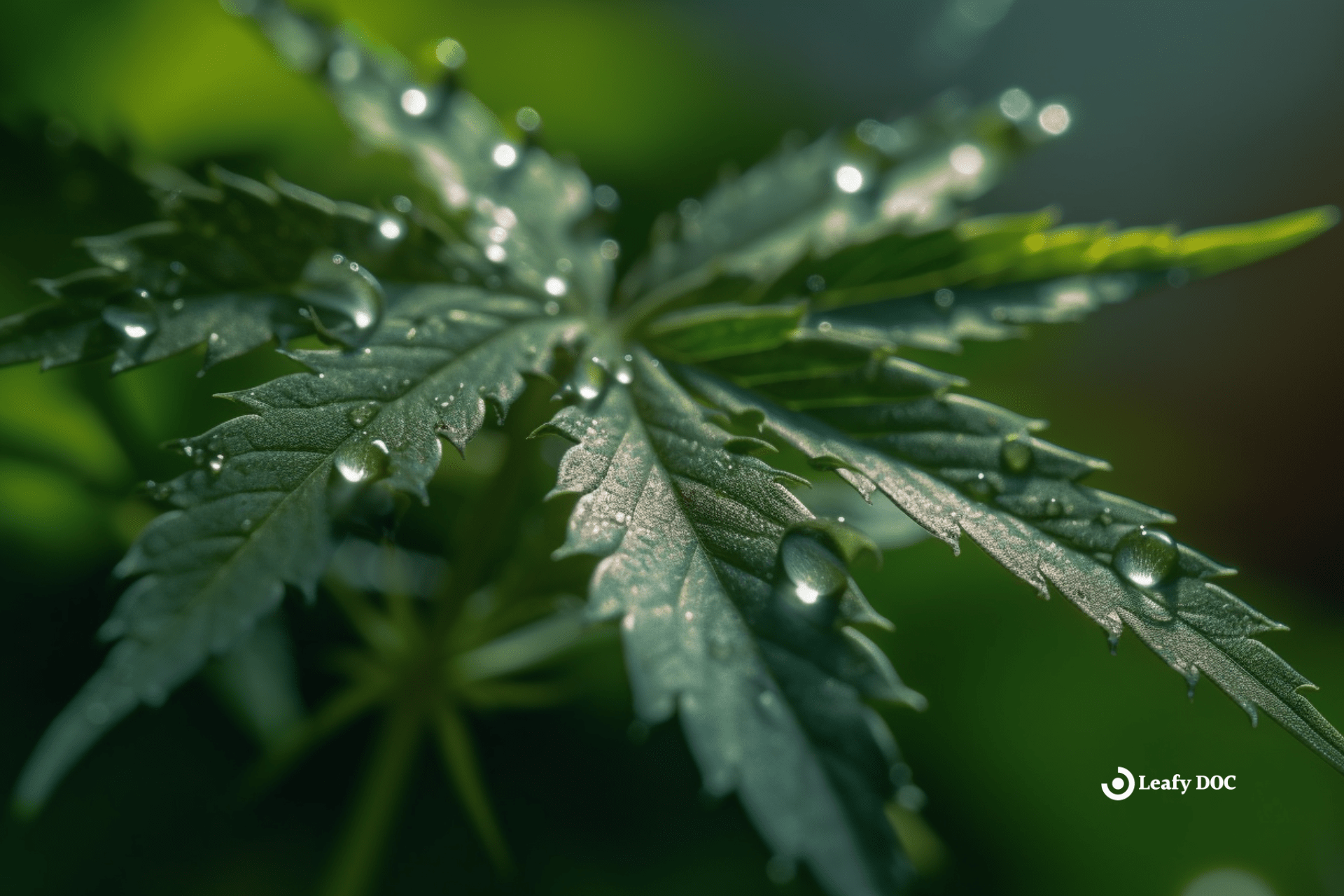
Marijuana has a unique anatomy with serrated, palmate leaves, a main central stem, and dense lateral branches that distinguish it from other similar-looking plants.
-
The plant grows through six key stages: germination, seedling, vegetative, pre-flowering, flowering, and harvest, each requiring different light, nutrients, and care.
-
Identifying plant sex is crucial because female plants produce potent buds, while male and hermaphrodite plants can pollinate and reduce flower quality.
-
Cannabis types differ by structure and effects. Sativa plants are tall and airy, Indica plants are short and dense, and Ruderalis plants are small and auto-flowering.
-
Buds and trichomes define quality since trichomes hold the THC, CBD, and terpenes that determine aroma, potency, and flavor.
-
Color and appearance signal plant health. Vibrant green or purple buds with dense trichomes show high quality, while yellow or brown tones suggest stress or nutrient issues.
-
Look-alike plants can cause confusion. Plants like cassava or chaste tree resemble cannabis but differ in leaf edges, flower color, and stem texture.
-
Proper harvesting and curing preserve quality. Harvest when pistils darken and trichomes turn milky or amber, then dry and cure buds in a cool, dark, and ventilated space.
Marijuana, also known as cannabis, is a plant that has gained significant attention in recent years due to its various uses and potential medical benefits. To accurately understand and appreciate this plant, it is crucial to delve into its intricate anatomy and distinctive characteristics.
In this article, we will explore the precise botanical terminology and scientific descriptions of a marijuana plant, providing insightful and detailed observations about its morphology, growth patterns, and reproductive features.
People often mistake other plants for cannabis, primarily due to their visual similarities at various growth stages. Certain plants have leaves or flowers that resemble those of Cannabis sativa, leading to confusion, especially among the untrained eye.
Several common shrubs, trees, and agricultural crops share features with cannabis. For instance, the familiar leaf pattern on some plants can look surprisingly similar to marijuana. This visual mimicry is why casual observers sometimes mistake cassava or other flowering shrubs for cannabis.
Moreover, the lack of distinct knowledge about plant characteristics contributes to this confusion. If you know what features to focus on, like leaf arrangement, vein patterns, or growth habits, it becomes easier to tell them apart.
- Leaf Shape and Pattern: Many plants have palmate leaves similar to cannabis.
- Growth Stages: At different growth phases, some plants exhibit similarities to marijuana.
- Knowledge Gap: A lack of familiarity with plant details often leads to misidentification.
Understanding these factors can help clarify why mix-ups occur and provide insight into distinguishing cannabis from other plants.
Anatomy of a Marijuana Plant
A marijuana plant, with its broad serrated leaves and dense clusters of flowers, is a visually striking and distinctive plant with a complex anatomy.
In terms of morphology, a marijuana plant typically has a main stem with branches that extend outward. The leaves are palmate, meaning they have multiple leaflets radiating from a central point, and they are serrated along the edges. The plant can reach heights of up to 20 feet, depending on the strain and growing conditions.
Natural vs. Trained Plant Structure
By nature, cannabis plants tend to grow in a single, upright column, often resembling a Christmas tree. This form allows the plant to maximize sunlight exposure from top to bottom. When left unaltered, the central stem develops one prominent main bud (often called a cola), while smaller buds form along the lower branches, sometimes resulting in less light reaching these areas.
However, many cultivators choose to shape, or “train”, their marijuana plants to improve light distribution and airflow throughout the canopy. Through techniques such as topping, low-stress training, or pruning, the plant’s form can change dramatically. Instead of a singular column, trained cannabis often spreads out into a wider, branched arrangement, similar to a candelabra. This method promotes even bud development across the plant, boosts overall yields, and helps ensure healthier growth by allowing better access to light and nutrients at every level.
Growth Stages and Visual Changes
When it comes to growth patterns, marijuana plants go through several stages, each with unique visual characteristics:
- Germination: This initial stage involves seeds maturing into shiny, brown specimens. Under the right conditions—dark, moist environments—these seeds sprout roots and cotyledon leaves, marking the transition to seedlings.
- Seedling Stage: Characterized by the emergence of traditional marijuana leaves with serrated edges, this stage requires 18-24 hours of sunlight and a delicate balance of moisture and humidity. The seedlings remain short with thick, vibrant green foliage, setting the stage for robust growth.
- Vegetative Stage: Here, the plant focuses on growing leaves and stems. It develops more leaves, nodes, and branches, requiring high amounts of nitrogen and other nutrients to support rapid growth. Variations between strains become apparent, with Sativa plants appearing taller and Indica plants more compact.
- Pre-Flowering: Lasting between 7 to 14 days, this stage is vital for sex determination. Female plants develop pistils, while males produce pollen sacs. It’s crucial to identify and manage these differences to prevent unwanted pollination.
- Flowering Stage: Transitioning to flower production, the plant requires a different nutrient balance, with increased phosphorus and potassium. The visual transformation includes color changes in pistils and trichomes, which signal harvest readiness.
- Harvest Stage: Finally, the plant enters the harvest stage, where the flowers are ready to be harvested and processed. This phase involves cutting and drying the plant, preserving its quality and enhancing flavor.
In terms of reproductive features, marijuana plants are dioecious, meaning they have separate male and female plants.
The female marijuana plant’s buds are highly prized for their rich concentration of cannabinoids like THC and CBD. These cannabinoids are found in the buds, where pistils (hair-like structures) and calyxes (protective coverings) develop. Male plants, which only produce pollen, are typically removed to prevent pollination, allowing the focus to remain on the female plants that produce more resin.
Female buds are covered in trichomes, small, resin-filled glands that significantly contribute to the plant’s potency. The density of these trichomes plays a major role in the strength and quality of the cannabis, making them a key feature for cultivators seeking high-quality, cannabinoid-rich products.
What Does a Marijuana Plant Look Like During the Germination Stage?
During germination, marijuana seeds transform into small, polished brown kernels. In this crucial phase, the seeds should be kept in a moist, dark environment to ensure optimal development. This setting encourages the emergence of a root, known as a radicle, as well as the cotyledon leaves.
These initial leaves differ from the typical fan-shaped marijuana leaves seen later in the plant’s life cycle. Though small and simple in structure, cotyledon leaves play a vital role in absorbing light energy, signaling the plant’s transition to the seedling stage. This stage marks the beginning of life for a cannabis plant, setting the foundation for its growth.
What Happens During the Pre-Flowering Stage of Marijuana Growth?
The pre-flowering stage in marijuana cultivation is crucial, as it sets the foundation for the plant’s reproductive phase. Typically lasting 7 to 14 days, this stage is primarily focused on sex determination, where the plant’s gender is identified.
Identifying Plant Sex
- Female Plants: Look for pistils, which are wispy, white hairs that appear from the buds. These hairs indicate that the plant is female and will eventually produce the desired flowers.
- Male Plants: Male plants will develop pollen sacs instead of pistils. These sacs are small, round structures that will release pollen. Shaped a bit like tiny bananas, pollen sacs are unique to male cannabis plants and play a crucial role in reproduction by containing and dispersing male pollen.
- Hermaphrodite Plants: Some plants may develop both pistils and pollen sacs. These plants are hermaphrodites, containing both male and female reproductive organs.
How to Identify a Hermaphrodite Marijuana Plant
Hermaphrodite marijuana plants have both male and female reproductive organs, displaying both pollen sacs and pistils. This can lead to unwanted seed formation in the buds, which can affect potency and flavor. Environmental stress, such as inconsistent lighting, nutrient imbalances, or temperature fluctuations, can trigger hermaphroditism.
How to Identify a Male Marijuana Plant
To accurately identify a male marijuana plant, look for specific characteristics:
- Taller and Less Bushy Appearance: Male marijuana plants often grow taller and are less bushy compared to female plants.
- Pre-Flowers and Sac Development: Male plants develop pre-flowers that appear as small, sac-like structures. These sacs contain pollen, crucial for fertilizing female plants, but undesirable in recreational or medicinal cultivation.
- No Buds: Unlike their female counterparts, male plants do not produce buds. Instead, they generate clusters of pollen sacs that lack the resinous and THC-rich characteristics of female buds.
- Early Identification: Male plants typically reveal their gender earlier than females, allowing growers to remove them quickly.
- Limited Trichome Production: Male marijuana plants generally produce fewer trichomes than females.
Why Identification Matters
It’s vital to identify and separate male and hermaphrodite plants during this stage to prevent unwanted pollination. If a female plant gets pollinated, it will start producing seeds rather than flowers, which is undesirable when cultivating for buds.
Action Steps
- As your plants enter the pre-flowering stage, carefully inspect them daily.
- Remove and isolate male and hermaphrodite plants to protect the females. By doing so, you ensure that the flowering stage progresses successfully, leading to a higher-quality harvest with no seeds.
Best Practices for Growing Marijuana During the Seedling Stage
Growing marijuana successfully requires attention to detail, especially during the vulnerable seedling stage. Here’s how to ensure your plants thrive:
- Provide Sufficient Light: Seedlings need plenty of light to grow robustly. Aim for 18 to 24 hours of light per day. LED or CFL lights are excellent options because they provide the necessary spectrum without excessive heat. Using a timer for consistent lighting is a good practice.
- Maintain Optimal Soil Conditions: Keep the soil moist, but not waterlogged. Water gently to avoid disturbing the young roots. Use well-draining, nutrient-rich soil to support healthy growth and monitor moisture regularly to maintain the right balance.
- Control Humidity and Temperature: Maintain humidity levels around 60-70% to encourage efficient water absorption. Ensure the temperature stays between 70-80°F (21-26°C) for the ideal growing environment.
- Observe Plant Characteristics: Healthy seedlings usually have short, sturdy stalks and thick, vibrant green leaves. Regular observation helps you spot any issues early and adjust care accordingly.
- Increase Leaf Count: As seedlings mature, the number of fingers on each leaf will naturally increase. Ensure consistent nutrients and light to support this development.
By following these guidelines, your seedlings will have a solid foundation for thriving into strong, healthy plants.
What Does a Sativa Plant Look Like?
Sativa plants are known for their tall, slender appearance, easily recognized by their height and structure. Growing as tall as 12 feet, they typically tower over their Indica counterparts, with an open and airy structure that promotes better air circulation.
Key Characteristics:
- Leaves: Sativa leaves are narrow and generally a lighter shade of green, which helps sunlight penetrate and sustain their long growth cycles.
- Height and Shape: These plants grow tall and lanky, a trait typical of their tropical origins. Their height and airy form make them ideal for outdoor cultivation, especially in areas with plenty of sunlight.
- Growth Environment: Sativa thrives in warm, equatorial climates, benefiting from long, sun-filled days.
How Sativa Differs from Indica and Ruderalis
While Sativa plants are tall and airy, Indica strains have a more compact appearance. Indica plants are shorter, with broader leaves and a darker green color. They grow densely, making them better suited to indoor or cooler, mountainous regions. Indica buds tend to be dense and compact, with a faster flowering cycle and deep green hues.
There’s also a third type: Ruderalis. Ruderalis plants are much smaller and hardier, usually featuring lower THC levels. They aren’t commonly grown for their psychoactive effects but are prized for their unique auto-flowering trait, making them useful in creating hybrids that flower automatically regardless of light cycles.
Flowering Time
Sativa strains take longer to flower compared to Indica. This extended flowering period contributes to their commonly reported uplifting and cerebral effects. Indica, on the other hand, matures more quickly, while Ruderalis is known for its rapid, automatic flowering regardless of season. This extended flowering period contributes to their commonly reported uplifting and cerebral effects.
By observing these visual cues, growers and enthusiasts can easily identify and appreciate the unique characteristics of Sativa plants.
Differences Between the Chaste Tree and Marijuana Plants
When distinguishing between the Chaste tree and marijuana plants, several key features can help you differentiate these two species:
- Leaf Structure:
- The Chaste tree boasts leaves with five leaflets arranged in a palmate style. In contrast, marijuana leaves are typically characterized by their serrated edges.
- Chaste tree leaves have smooth margins and often curl slightly at the tips, whereas marijuana leaves display a more jagged appearance.
- Flower and Fruit Production:
- The Chaste tree is known for its vivid, light purple flowers and prominent berries that grow in clusters.
- Marijuana plants, however, produce buds that are generally less conspicuous and more muted compared to the eye-catching flowers of the Chaste tree.
- Overall Appearance:
- While both plants can have similar leaf shapes at a glance, the Chaste tree’s overall presentation is more ornamental due to its floral displays.
- The marijuana plant is primarily noted for its distinctively shaped leaves.
By focusing on these distinguishing traits, such as leaf edge and texture, as well as floral differences, it’s easier to correctly identify and appreciate each plant’s unique characteristics.
Leaves and Leaflets
Take a moment to observe the vibrant green leaves and leaflets of a marijuana plant, as they gracefully fan out and capture the sunlight. The leaf structure of a marijuana plant consists of compound leaves, which are composed of multiple leaflets attached to a central stalk, known as the petiole. These leaflets are arranged in an opposite pattern, meaning they are positioned directly across from each other on the stem. Each leaflet has a serrated edge, giving it a jagged appearance. The leaflets themselves are elongated and have a pointed tip, with a length that can vary depending on the specific marijuana strain.
To further explore the leaf structure of marijuana plants, let’s take a look at the following table:
| Leaf Structure | Description |
|---|---|
| Compound Leaves | Composed of multiple leaflets attached to a central stalk |
| Opposite Arrangement | Leaflets positioned directly across from each other on the stem |
| Serrated Edge | Jagged edge of each leaflet |
| Elongated Shape | Leaflets are elongated with a pointed tip |
| Length Variation | Leaflet length can vary depending on the marijuana strain |
When trying to differentiate plants that resemble cannabis, it’s essential to examine certain key features. For each similar plant, specific characteristics can help in identifying them correctly:
Leaf Color and Texture
- Japanese Maple: These leaves transition to red, pink, and purple hues by late spring or summer, unlike the consistent green or purple tones of cannabis leaves. Also, Japanese maple leaves are smooth and hairless, while cannabis leaves are covered with fine hairs.
- Marigold: Look for the bright yellow flowers that marigolds produce, which differ from the green or purple buds of cannabis. Furthermore, marigold leaves attach directly to the stem, while cannabis leaves are part of a compound structure.
Flower Structure and Color
- Sunn Hemp: This plant shows off bright yellow flowers in contrast to cannabis’s green or purple buds. Also, its leaves are singular and elliptical, not compound like cannabis.
- Coralbush: Notice the bright pink flower clusters it releases. The leaves are lobed rather than divided into leaflets, a hallmark of cannabis.
Stem Characteristics
- Hibiscus: The woody stem of the Hibiscus coccineus sets it apart from the green, softer stems of cannabis. Moreover, the flowers come in vibrant yellow or scarlet shades.
Leaf Structure
- Chaste Tree: Its leaves are smooth and curl slightly under at the ends, opposing the serrated edges of cannabis leaves.
Unusual Misidentifications
Sometimes, unexpected plants can be misidentified, as happened with an okra plot mistaken for cannabis. A careful look would reveal that okra lacks the distinct buds associated with cannabis.
By focusing on these specific features, leaf color, flower structure, stem toughness, and general growth patterns—you can effectively distinguish between cannabis and its look-alikes. Keep these characteristics in mind to avoid any potential mix-ups.
Comparing Cassava and Cannabis Leaves: Similarities and Differences
When comparing the leaves of cassava and cannabis, there are some interesting similarities and key differences that stand out.
Similarities:
- Leaf Shape: Both cassava and cannabis leaves exhibit a palmate shape, which can cause some confusion at a glance. This broadly means that the leaves spread out from a central point, resembling an open hand.
- Lack of Petals in Flowers: Neither plant produces flowers with traditional petals. Cassava has colorful sepals, making its flowers striking, whereas cannabis flowers are more subdued with green-white sepals.
Differences:
- Leaf Detailing: A critical distinction is in the leaflets. Cannabis leaves are divided into separate, distinct leaflets, often giving them a characteristic jagged appearance. In contrast, cassava leaves are lobed but remain a single, smooth-edged unit without divided leaflets.
- Latex Production: Cassava releases a sticky, white latex when its leaves are damaged, akin to okra. This is not a trait shared by cannabis, which does not exude any latex.
These attributes highlight that while they may share a superficial resemblance, cassava and cannabis have distinct characteristics that set them apart in the plant world.
Stems and Branches
With its sturdy, green stems and sprawling branches, a marijuana plant resembles a miniature tree. The stem structure of a marijuana plant consists of a main central stem, known as the main stem or the stalk, which extends vertically from the soil and supports the entire plant.
From the main stem, numerous lateral branches emerge, forming the branching structure of the plant. These branches grow in a somewhat irregular pattern, with some branches growing vertically upwards while others grow at more oblique angles. The stems of a marijuana plant are typically thick and woody, providing strength and support to the plant as it grows and develops.
Branch growth patterns in marijuana plants can vary depending on the specific strain and growing conditions. However, in general, marijuana plants exhibit a sympodial branching pattern. This means that the growth of the plant is characterized by the formation of lateral branches from the main stem, with each branch having the potential to grow into a new main stem.
As the plant grows, new branches continue to emerge from the main stem, creating a bushy and dense canopy of foliage. In addition to their structural role, the stems and branches of a marijuana plant also play a crucial role in the reproductive process. The nodes, or the points where leaves and branches emerge from the stem, are essential sites for the formation of flowers and ultimately the production of seeds or cannabinoids. These nodes act as junctions along the main stem, marking where growth points originate, whether that’s a new branch, leaf, or eventually a flower cluster. In between each node, you’ll find the internodes: the stem segments that span the space between two nodes. The length of these internodes determines how spaced out the branches and leaves will be, which can influence the plant’s overall shape and ability to capture light.
Understanding both nodes and internodes is vital for growers, as they not only provide structural support but also dictate where future growth and flowering will occur. The density and placement of nodes can vary depending on the strain and growing conditions, leading to different branching patterns and plant architectures.
What Does a Baby Marijuana Plant Look Like?
Recognizing the features of a baby marijuana plant is an essential step in cultivating healthy cannabis. The initial stages of life are vital for establishing a sturdy plant foundation.
During germination, the plant begins its journey with the emergence of small, tender leaves. These leaves are the first indicators of growth, marking the transition to the seedling stage.
Key Features of a Baby Marijuana Plant
- Cotyledon Leaves: These are the initial leaves that appear on the plant. Unlike the iconic serrated leaves seen on mature plants, cotyledon leaves are rounder and provide the first nourishment for growth.
- Root Development: At this early stage, the plant develops its root system. A primary root, known as the radicle, sprouts to anchor the plant and begin nutrient absorption.
- Shed Seed Casing: As the plant grows, it naturally discards its seed casing, unveiling the first set of leaves. This period is delicate and requires careful attention to ensure successful development.
- Structure and Care: Young marijuana plants appear compact and fragile. Providing sufficient sunlight, water, and nutrients during this time is crucial for supporting strong and healthy growth.
In summary, a baby marijuana plant may not look like much initially. However, these small features, cotyledon leaves, developing roots, and the emerging structure—are critical indicators of a plant’s potential. Providing optimal care in this phase sets the stage for a thriving cannabis plant.
Understanding the Leaf Count of a Marijuana Plant
When examining a marijuana plant, the leaf structure is one of its most distinctive features. Let’s break down the leaf development process:
Leaf Development Stages:
- Seedling Stage: The first pair of leaves the plant produces are cotyledons (single-blade leaves), which help with early photosynthesis.
- Mature Stage: As the plant grows, it develops multi-fingered leaves. These mature leaves typically have 5 to 9 fingers, with 7 being the most common.
Influencing Factors: Several elements can affect the leaf count and structure:
- Genetics: Different cannabis strains have unique genetic traits that influence leaf count and shape.
- Growing Conditions: Light, soil quality, and water availability impact leaf development.
- Pruning Practices: Growers’ techniques can shape leaf structures.
In general, a standard marijuana plant will display leaves with 5 to 9 fingers. However, various factors can cause slight variations. Understanding these differences provides valuable insights into the plant’s overall health and growth conditions.
Understanding Marijuana Plant Colors
The color of a marijuana plant provides important insights into its characteristics. Green leaves typically indicate high THC content, making them ideal for recreational or medicinal use. Yellow, orange, and brown leaves may suggest aging or stress, often signaling nutrient deficiencies. Purple and red leaves are usually ornamental and contribute to aesthetic appeal rather than potency.
How to Identify High-Quality Cannabis Buds
High-quality cannabis buds can be recognized by several key visual and physical traits.
Color and Appearance
Top-shelf marijuana typically has a vibrant green color, often accented with shades of purple, orange, or red depending on the strain. These buds should look fresh, not faded or brown, and should display a healthy sheen.
Trichome Coverage
A thick layer of visible trichomes, the small, crystal-like resin glands, is one of the best indicators of potency. These trichomes are responsible for producing cannabinoids and terpenes, contributing to both aroma and strength.
Bud Structure
Quality buds are dense, compact, and well-trimmed. They should feel slightly sticky due to the resin but not damp or brittle. Loose, airy, or leafy buds may indicate poor cultivation or improper curing.
Aroma
A strong, distinct aroma, ranging from citrus and floral to earthy or skunky, is another sign of a well-cured, high-quality cannabis bud. A dull or hay-like smell may suggest the flower is old or poorly stored.
By observing these traits, color, trichome density, structure, and scent, you can more confidently distinguish high-quality cannabis from lower-grade alternatives.
Flowers and Buds
The flowers and buds of a marijuana plant are the most recognizable and sought-after parts of the plant. They develop in clusters at the nodes of the branches and are typically covered in resinous trichomes.
These flowers, often referred to as “buds,” play a crucial role in the plant’s life cycle. Their main purpose is reproduction, as they house all of the female reproductive organs. In addition, they contain the highest concentration of cannabinoids and terpenes—the compounds responsible for cannabis’s effects, aroma, and flavor. The dense coating of trichomes gives the buds their sticky, frosted appearance and is a key indicator of potency.
Understanding the structure and function of marijuana flowers helps explain why they are the focus of cultivation and harvest, and why they’re prized by growers and enthusiasts alike.
Each bud is made up of tightly packed calyxes, the small leaf-like structures surrounding the reproductive organs. These calyxes are coated with trichomes, tiny resin glands responsible for producing cannabinoids like THC and CBD, as well as aromatic terpenes. The calyxes form the outer skin of the female flower’s reproductive system, safeguarding the delicate organs within from environmental stressors and potential threats. Not only do they provide crucial protection, but they also play a vital role in supporting seed development if the flower is pollinated.
Bracts: The Unsung Protectors
Bracts are small, leaf-like structures found at the base of female cannabis flowers. Though easy to overlook, these tiny coverings play a crucial role in shielding the reproductive parts of the plant, offering the first line of defense for developing buds. In addition to their protective function, bracts are densely covered with trichomes, those same resin glands responsible for producing potent cannabinoids and fragrant terpenes. As a result, bracts significantly contribute to both the aroma and strength of the finished flower, quietly enhancing the overall quality and character of each bud.
Key Flower and Bud Structures
- Cola: The main bud cluster, typically located at the top of the plant. It contains the highest density of flowers and is often the most resinous.
- Pistils: Thin, hair-like structures emerging from the calyxes. They change color from white to orange, red, or brown as the flower matures and are used to identify bud maturity.
- Sugar Leaves: Small leaves coated in trichomes that grow within the bud. Although often trimmed, they retain potency and are used for making extracts and edibles.
- Fan Leaves: Large, broad leaves used for photosynthesis. These are typically removed before harvest, as they contain minimal cannabinoid content. Fan leaves play several crucial roles throughout the cannabis plant’s life. Found mostly on the internodes—the sections of stem between two nodes, these leaves are responsible for:
- Absorbing light to power photosynthesis
- Facilitating transpiration and gas exchange
- Absorbing CO₂ from the environment
- Storing sugars and minerals vital for healthy growth
- While essential during the growing phase, fan leaves are generally trimmed away before harvest since they lack significant cannabinoid concentrations.
Understanding the Stigma vs. The Pistil
It’s common to hear the terms “pistil” and “stigma” used interchangeably, but they actually refer to different parts of the cannabis flower’s anatomy.
- Pistil: The pistil is the reproductive organ of the female cannabis flower. It includes several components, most notably the ovule at the base and the slender hair-like structures that protrude from the bud.
- Stigma: The stigma is the actual tiny, hair-like tip you see emerging from the pistil. Its primary role is to capture pollen from male plants during fertilization.
In summary, while the pistil refers to the entire reproductive structure, the stigma is just one part of it, the visible, often colorful “hairs” that change hue as the plant matures. Recognizing the difference helps growers better assess the stages of bud development and the overall health of the plant.
Key Features of Cannabis Buds Compared to Other Flowers
Cannabis buds are dense and cone-shaped, often covered with tiny sugar leaves coated in sticky resin. As the plant matures, the pistils—those hair-like strands on female flowers, darken from white to deep orange or amber, signaling the buds are ready for harvest.
Unlike bright garden flowers like marigolds or hibiscus, cannabis doesn’t produce colorful petals. Instead, its beauty comes from the trichomes—crystal-like glands that give buds a frosty, sparkling look while producing cannabinoids and terpenes.
Buds grow in tight clusters called colas along the branches, giving cannabis a compact, bushy appearance. You’ll see mostly green tones, though some strains may show hints of purple or red.
While other plants show off with bold blooms and petals, cannabis flowers are subtle. Their value lies in potency, aroma, and the resin-rich trichomes that define their signature look.
Trichomes:
Trichomes are tiny, crystal-like structures that blanket the surface of the cannabis flower. These glandular outgrowths not only give the buds their frosty appearance but also play a critical role in the plant’s value and potency. Trichomes are responsible for producing and storing cannabinoids and terpenes—the compounds behind the plant’s distinctive aroma and effects. When viewed under magnification, trichomes resemble sparkling, miniature mushrooms, and their density is often an indicator of the quality of the flower.
Trimming and Harvesting
Trimming and harvesting methods play a crucial role in ensuring the flowers and buds are properly handled and preserved. Trimming involves removing any excess leaves and foliage from the buds, while harvesting involves carefully cutting the plant at the right time to achieve the desired potency and flavor.
Steps for Harvesting Marijuana Plants
Harvesting marijuana begins with cutting the plant into smaller branches for drying. It’s important to hang the branches upside down in a cool, dark room to prevent fungus and bacteria growth, which can compromise your yield.
Drying and Curing Process
The drying and optional curing process are essential for preserving the cannabis, enhancing both flavor and burn quality. To ensure a smoother smoking experience, maintain a controlled humidity level between 40% and 50% during drying. This helps prevent microbial growth and contributes to the overall quality of your harvest.
Determining Harvest Readiness During Flowering
Knowing when to harvest marijuana during the flowering stage can make a big difference in potency and overall quality. Here are key signs to watch for:
Pistils and Trichomes:
Look at the pistils (the hair-like strands on buds). They start white and darken as the plant matures. More importantly, check the trichomes, the frosty, crystal-like glands on the buds and nearby leaves. Clear trichomes mean it’s too early. Milky ones signal peak THC, while amber ones indicate a higher CBD content and a more relaxing effect.
Indoor Growing Tips:
- Temperature: Keep it between 65°F and 85°F.
- Humidity: Aim for 40–50% to prevent mold and support bud growth.
- Lighting: Use 300–400-watt grow lights to mimic sunlight and support flower production.
Outdoor Growing Tips:
- Climate: Warm, sunny weather helps the plant thrive.
- Nutrients: Use bloom-specific fertilizer during flowering for healthy bud development.
With these cues, you can harvest at just the right time for the effects you want.
How to Identify Poor-Quality Cannabis (Dirt Weed)
Recognizing low-quality or poorly cultivated cannabis, commonly referred to as “dirt weed”, is essential for ensuring a good user experience. Several signs can help you assess cannabis quality before consumption.
Appearance
Poor-quality cannabis often appears brown, dull, or uneven in color. It may contain excess stems, seeds, or have a loose, shaggy structure. In contrast, healthy cannabis has vibrant green hues with orange or purple accents.
Trichomes
High-quality cannabis is coated in frosty, crystal-like trichomes. A lack of visible resin or a dry, dusty appearance suggests low potency and poor cannabinoid content.
Aroma
A musty, moldy, or hay-like odor is a red flag. This can indicate improper drying, curing, or storage. Quality cannabis typically has a strong, complex scent, such as citrus, pine, or earthy tones.
Texture
When gently pressed, the buds should feel slightly sticky and resilient. Overly dry or crumbly texture, or excessive moisture, can signal improper curing or potential mold contamination.
Taste and Smoke Quality
Poorly grown or stored cannabis may produce a harsh or burnt taste, sometimes with chemical or grassy flavors. In contrast, well-cured buds provide smoother, more flavorful smoke.
By recognizing these indicators, you can better avoid low-grade cannabis and choose buds that offer both quality and safety.
Exploring the Aromas and Flavors of Marijuana
The smell of marijuana is iconic and varies widely depending on the strain. Common aromas include earthy, woody scents, fruity and sweet notes, and spicy or herbal undertones. Some strains may even have hints of citrus, berries, or tropical fruits, while others exude rich, musky or woody fragrances.
As for flavor, it can range from citrus and berry to vanilla and cream, or even pepper and pine, offering a unique experience for each user. These sensory profiles are influenced by the strain and its growing conditions, providing a variety of olfactory and gustatory experiences.
Distinguishing Features of the Texas Star Hibiscus Compared to Cannabis
At a glance, the Texas Star Hibiscus and cannabis can appear remarkably similar due to their long, slender stems and textured, serrated leaves. However, a closer inspection reveals several key differences that can help you tell them apart.
- Stem Composition: One of the most notable distinctions is found in the stem. The Texas Star Hibiscus features a woody stem, which offers a more rigid structure. In contrast, the stem of a cannabis plant is typically green and soft, giving it a more flexible appearance.
- Leaf Characteristics: While both plants have leaves with serrated edges, the leaves of the Texas Star Hibiscus often appear droopier than those of cannabis. This slight sag in the leaves can be a telling sign when trying to differentiate between the two.
- Flowering: Another clear differentiator emerges in the summertime, when the Texas Star Hibiscus produces vibrant crimson or white flowers. These blossoms are absent in cannabis, providing a vivid contrast during the flowering period.
By examining these distinguishing features, you can easily identify the Texas Star Hibiscus from cannabis, ensuring that there’s no mix-up between these two botanically fascinating plants.
Roots and Root System
The roots of a marijuana plant are critical for its overall growth and nutrient absorption. The root system of a marijuana plant consists of a main taproot that extends vertically into the soil and lateral roots that spread horizontally. The taproot is the primary structural component of the root system and acts as an anchor, providing stability to the plant. It also plays a crucial role in nutrient absorption, as it is responsible for taking up water and minerals from the soil.
The root structure of a marijuana plant is extensive and intricate. The lateral roots branch out from the taproot and form a dense network in the soil. These roots are thin and fibrous, allowing for efficient nutrient uptake. The root tips are covered in tiny root hairs, which increase the surface area for absorption. These root hairs are responsible for absorbing water and nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which are essential for the plant’s growth and development.
The marijuana plant’s roots have specialized cells called root cortex cells that are responsible for the uptake and transportation of nutrients. These cells have tiny projections called root hairs, which increase the surface area available for nutrient absorption. The roots also have a symbiotic relationship with mycorrhizal fungi, which help enhance nutrient uptake by increasing the surface area of the root system.
How to Identify a Hemp Plant
Identifying a hemp plant involves examining distinct features that set it apart from other varieties of Cannabis sativa, such as marijuana.
- Leaf Structure: Hemp plants have narrow leaves that are typically concentrated at the top of the plant. This structure is one of the key indicators for distinguishing hemp from marijuana.
- Height and Build: Hemp plants are tall and slender, often towering over marijuana plants, which are usually shorter and bushier in comparison.
- THC Content: The THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) content in hemp is low, as it is cultivated for industrial uses like fiber production and does not produce the psychoactive effects associated with marijuana.
- Stem and Fiber: Hemp’s stems are robust and strong, ideal for industrial uses such as textiles, rope, and more.
- Bud Appearance: Hemp’s flowers are sparser and less resinous compared to marijuana’s dense, resin-filled buds, as hemp focuses more on fiber and seed production rather than high THC content.
By observing these features, you can easily identify hemp plants and distinguish them from other cannabis varieties based on their purpose and physical traits.
Are you curious about which plants might be mistaken for marijuana? Here’s a detailed guide to help you identify plants that look like marijuana at different growth stages.
1. Japanese Maple (Acer palmatum)
Often mistaken for cannabis when young, Japanese maple trees have slim stems and bright green palmate leaves. However, unlike cannabis, these leaves transition into vibrant reds, pinks, and purples, and are hairless.
2. Southern Marigold (Tagetes minuta)
Known for its culinary and medicinal use, Southern marigold can resemble marijuana in its early stages with its long, serrated leaves and similar size. However, marigolds produce yellow flowers and have singular leaves.
3. Sunn Hemp (Crotalaria juncea)
Sharing a similar thin structure with cannabis, sunn hemp is used as green manure. It can be distinguished by its bright yellow flowers and singular, elliptical leaves instead of compound ones.
4. Coral Plant (Jatropha multifida)
The coral plant, with its palm-shaped leaves, can look misleadingly like marijuana. It differs with its lobed (not divided) leaves, bright pink flowers, and a distinctive scent.
5. Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus)
Famed for its edible seed pods, okra can resemble cannabis due to its palmate green leaves. Unique to okra are its large pods and white or yellow flowers—unlike cannabis’s green or purple buds.
6. Cassava (Manihot esculenta)
This starchy root plant is visually similar to marijuana with palm-like leaves. Key differences include its smooth leaf edges and the production of white latex when damaged.
7. Spider Flower (Cleome hassleriana)
With long, spiky leaves, spider flowers can mimic cannabis during early growth. Look for less prominent toothed margins and a musky odor from their glandular hairs.
8. Texas Star Hibiscus (Hibiscus coccineus)
At the start of its growth cycle, the Texas Star Hibiscus mimics marijuana’s slender stems and textured leaves. However, it becomes easily recognizable with its woody stems and vivid flowers.
9. Kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus)
Kenaf’s botanical name hints at its resemblance to cannabis. While they look alike when young, kenaf matures into a plant with bright flowers and lobed leaves with varied shapes.
10. Chaste Tree (Vitex agnus-castus)
This plant, famous for its medicinal properties, is often mistaken for cannabis due to its palmate leaf arrangement. Distinguishing features include smoother leaf edges and distinct light purple flowers.
Understanding these differences can prevent confusion and help appreciate the diversity among plants that resemble cannabis in various aspects.
Discover Plants Often Confused with Cannabis
When you think of cannabis, the iconic leaf shape might come to mind. However, several plants bear a striking resemblance to it, which can lead to confusion. Here’s a rundown of plants often mistaken for Cannabis sativa:
1. Japanese Maple (Acer palmatum)
Originating from Asia, the Japanese maple has young saplings with bright green, slender leaves that mimic the marijuana plant. As these trees mature, the leaves transform into hues of red, pink, and purple, distinguishing them from cannabis.
2. Southern Marigold (Tagetes minuta)
Native to Central America, this plant is sometimes mislabeled as cannabis due to its long, serrated leaves. Key differences include its small yellow flowers, unlike the green or purple cannabis buds.
3. Sunn Hemp (Crotalaria juncea)
Used as a green manure crop, sunn hemp features thin, green leaves reminiscent of cannabis. It stands apart with its bright yellow flowers and singular, elliptical leaves, unlike the compound leaflets of cannabis.
4. Coral Plant (Jatropha multifida)
Hailing from Mexico and the Caribbean, the coral plant’s palm-shaped leaves mislead some into thinking it’s marijuana. The unpleasant odor and bright pink flowers help differentiate it.
5. Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus)
A culinary staple in tropical regions, okra shares a similar green, palmate leaf shape with cannabis. Its distinct large flowers and seed pods, however, set it apart.
6. Cassava (Manihot esculenta)
An important carbohydrate source from South America, cassava’s lobed leaves can appear cannabis-like. Smooth leaf edges contrast with the jagged look of cannabis leaves, aiding identification.
7. Spider Flower (Cleome hassleriana)
This North American plant is comparable to cannabis when not in bloom, with long, spiky leaves. However, its musky scent and pink flowers are clear indicators that it’s not cannabis.
8. Texas Star Hibiscus (Hibiscus coccineus)
The Texas Star Hibiscus has slender stems and serrated leaves, resembling marijuana. Yet, its vivid crimson or white blossoms make it easily distinguishable.
9. Kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus)
Closely linked to cannabis in appearance during its initial growth period, kenaf features lobed leaves and vibrant flowers, distinguishing it from the subtler cannabis plant.
10. Chaste Tree (Vitex agnus-castus)
This Mediterranean plant has early-stage growth that may be confused with cannabis due to its five-leaflet arrangement. The smooth leaf surface and purple flowers differentiate it from marijuana.
With these botanicals, it’s easy to see how misconceptions arise. Each has unique characteristics that, upon closer inspection, help differentiate them from cannabis.
Conclusion
A marijuana plant exhibits a distinct anatomy that is characterized by its leaves and leaflets, stems and branches, flowers and buds, and roots and root system.
The leaves of a marijuana plant are compound, meaning they’re composed of multiple leaflets attached to a central stalk. These leaflets are typically serrated and have a pointed tip. The stems of a marijuana plant are sturdy and erect, branching out to support the growth of the plant. The flowers and buds of a marijuana plant are the most recognizable and sought-after parts of the plant. They develop in clusters at the nodes of the branches and are typically covered in resinous trichomes. The roots and root system of a marijuana plant are essential for absorbing water and nutrients from the soil.
By studying the structure of a marijuana plant, you can gain a comprehensive understanding of what a marijuana plant looks like and therefore how it grows and thrives.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I identify a marijuana plant?
A marijuana plant can be identified by its serrated, palmate leaves with 5 to 9 narrow fingers, a tall central stem, and dense lateral branches. The plant also produces a strong aroma and, in female plants, sticky buds covered with tiny crystal-like trichomes that contain cannabinoids such as THC and CBD.
What are the main growth stages of a marijuana plant?
A marijuana plant grows through six main stages: germination, seedling, vegetative, pre-flowering, flowering, and harvest. Each stage requires specific care, including proper lighting, nutrients, and humidity levels to ensure healthy growth and potent buds.
How can I tell the difference between male and female marijuana plants?
Female marijuana plants develop white pistils and produce resinous buds rich in cannabinoids. Male plants, on the other hand, grow small pollen sacs instead of pistils. It’s important to separate male plants early to prevent pollination, which can reduce the quality and potency of the female buds.
Last Updated: November 5, 2025
Get Approved for Your Medical Marijuana Card in Minutes!

Get Your Medical Card
Connect with a licensed physician online in minutes
-
Naim-Feil, E. (2023). The cannabis plant as a complex system. Plants, 12(3), 493. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12030493 MDPI
-
Punja, Z. K., Sutton, D. B., & Kim, T. (2023). Glandular trichome development, morphology, and maturation are influenced by plant age and genotype in high THC-containing Cannabis sativa L. inflorescences. Journal of Cannabis Research, 5, 12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s42238-023-00178-9 BioMed Central
-
Spitzer-Rimon, B., et al. (2019). Architecture and florogenesis in female Cannabis sativa. Frontiers in Plant Science, 10, 350. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00350 Frontiers
-
Livingston, S. J., et al. (2020). Cannabis trichomes: What are they? The Plant Journal. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.14516 Wiley Online Library
-
Tahir, N., Shahbazi Raz, F., Rondeau-Gagné, S., & Trant, J. F. (2021). The biosynthesis of the cannabinoids. Journal of Cannabis Research, 3(7). https://doi.org/10.1186/s42238-021-00062-4 PMC
-
Raman, V., Lata, H., Chandra, S., & Khan, I. A. (2017). Morpho-anatomy of marijuana (Cannabis sativa L.). ResearchGate. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/318020563_Morpho-Anatomy_of_Marijuana_Cannabis_sativa_L ResearchGate
-
Lata, H., et al. (2021). Cannabis glandular trichomes: A cellular metabolite factory. Frontiers in Plant Science, 12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.721986 Frontiers
-
Hill, K. P., et al. (2022). The morphological and anatomical variability of the stems of fibre and non-fibre type hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) genotypes. Industrial Crops and Products, 170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2021.114606 ScienceDirect
-
Romano, E., & Hazekamp, A. (2022). A comprehensive review on Cannabis sativa ethnobotany, chemical composition and biological activities. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 13, 792539. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.792539 PMC
-
Extension, University of Nebraska. (n.d.). Hemp basics: Anatomy of a female hemp plant. UNL Extension. https://extension.unr.edu/publication.aspx?PubID=4479
Like This Article?
Share with your friends
Table of Contents
Keep Reading
-
Unlocking The Uses Of CBD Oil For Wellness
Unleash the power of nature with CBD oil and discover its incredible uses for your overall wellness. Click now to unlock a healthier, happier you with the benefits of CBD oil.
-
Discover The Best Cannabis Strains For Exercise
Enhance your workout routine with the best cannabis strains for exercise! Discover how these powerful options can elevate your fitness game. Click here to find out more and take your workouts to the next level!
-
Consult A Medical Marijuana Doctor Online
Unlock the benefits of medical marijuana with a click! Consult an expert online and discover the convenience of alternative medicine from home. Don’t miss out, book your appointment with a medical marijuana doctor today.



